Just as we learnt in the inspiring Gamechangers Netflix documentary in 2019 how the carbon dating of human bones revealed that the ancient gladiators ate a primarily vegetarian diet for strength; so we found this very relevant article in the April 2021 issue of New Scientist fascinating –
Bronze Age dogs ate little meat and had to feed on cereals instead
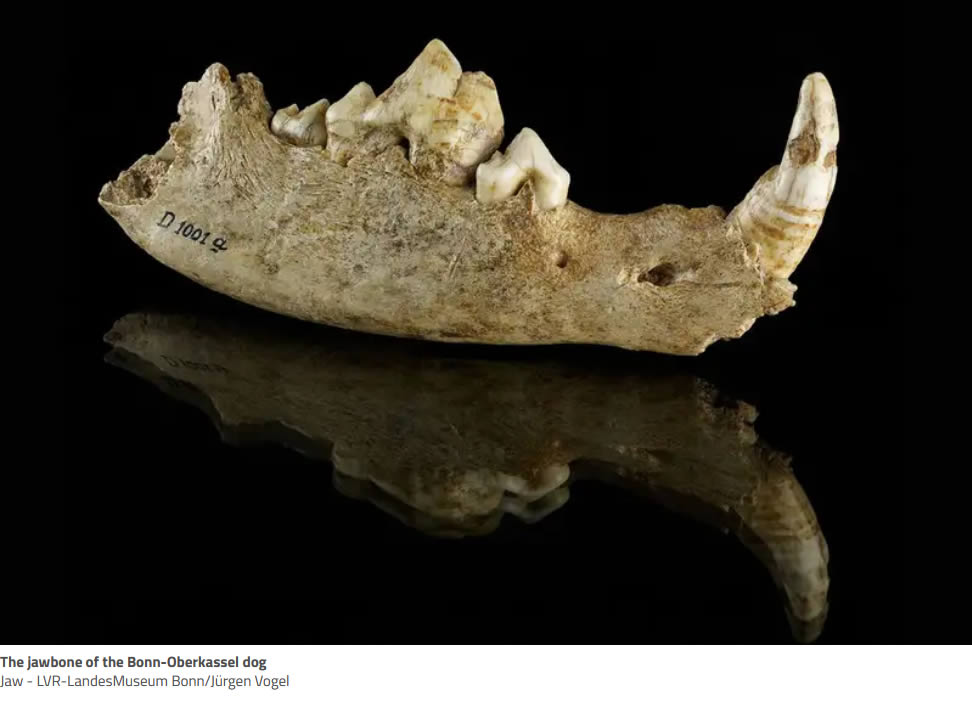
Many early domestic dogs ate almost no meat. Dogs living around 3000 years ago in what is now Spain were instead fed cereals, such as millet, by their owners.
Although the diet may reflect the fact that meat was relatively scarce among human societies at the time, feeding dogs with cereals could have been advantageous, says Silvia Albizuri at the University of Barcelona in Spain. It may have been a way to ensure the dogs had plenty of energy for the strenuous work of herding and guarding livestock, she says, particularly since these dogs “were not pets as we conceive them nowadays”.
Dogs were domesticated from wolves in Europe and Asia within the past 40,000 years. Wolves are carnivores, getting most of their nutrition from meat.
Albizuri and her colleagues studied the remains of 36 dogs from Can Roqueta, an archaeological site near Barcelona. It lies on a plain near the coast and was inhabited from the Stone Age onwards. The dogs lived in the Bronze Age and Iron Age, between 1300 and 550 BC, and had been buried in pits.
The researchers obtained protein from the dogs’ bones and focused on the carbon and nitrogen atoms in the samples, each of which exist in two forms called isotopes. Different foods have varying ratios of carbon and nitrogen isotopes, and this influences the makeup of the protein – so studying the isotopes in the protein gives an indication of what the animals ate.
Read more: Humans may have domesticated dogs by accident by sharing excess meat
The dogs’ diets differed considerably. While nine of them ate plenty of meat and 10 were omnivorous, the rest ate mostly plants – and some had isotope ratios that could barely be distinguished from those of the cattle they once guarded.
The finding adds to the evidence that many early domestic dogs ate little meat, says Albizuri. This trend began with the advent of farming. “When human societies began to domesticate plants during the Neolithic period, hunting decreased and the human diet was based mainly on vegetables,” she says. “Dogs began to be fed on plants, mainly cereals.”
This has had effects on domestic dogs today, says Albizuri. Grains are easier to chew than raw meat, so they don’t need their jaw muscles to be as strong as those of wolves. What’s more, their jaw bones have changed shape and their teeth have shrunk. Their digestive systems have also changed. “Dogs have more genes involved in starch metabolism than wolves,” she says.
However, not all dogs have undergone these changes. “Societies that maintained a subsistence system based on hunting and gathering, mainly those located in cold areas, continued to feed their dogs with meat,” says Albizuri. “In today’s dog breeds, there are significant genetic differences related to starch metabolism.”
Article courtesy of Magazine Issue new Scientist, published 10th April 2021

Should All Dogs Go Plant-Based?
Dr Arielle Griffiths is interviewed on live TV Channel 5 and shows Jeremy Vine how delicious vegan dog food is
Beautiful Loki the Vizsla loves Give A Dog A Bean
He’s on Solo Vegetal, as I’ve always been a dry food feeder for convenience, but he goes absolutely nuts for your Give A Dog A Bean!
Oldest living dog Bobi dies aged 31!
How your dog can live as long as Bobi eating a wholefood balanced diet as oldest vegan dog lived until she was 25!
The kindest pet owner you can be
At this noisy time of fireworks, and at anytime, we advise on how to be the kindest pet owner that you can be!
Surrey Vet School Students Are Inspired
Hi Arielle, Thank you so much for coming this evening, it was a fantastic talk! We’d love to have you back to do another talk! Many thanks VetSoc Surrey
The transformation was unbelievable!!
A fascinating discovery by top Vet Oncologist Dr Clare Knottenbelt who put her own dog Jumble on a plant-based diet
Pets At Home Commits To Net Zero Goals
Pets At Home Commits To SustainabilityThis article from October 23 is enormously reassuring in how the big players such as Pets At Home are moving forward - Supporting sustainable pet owners An example of these kinds of environmental commitments can be found at...
Arthur the Diabetic Labrador thrives on his plant-based diet
Just as in humans, the best diet when suffering from diabetes, is a balanced fibre rich, plant-based diet
I’m proud to be the vegan owner of a healthy vegan Cockapoo
We can all be just so proud of what we are doing, and together let’s be the ones to pioneer what Prof Knight has started
I had previously tried him with Yumove tablets and saw no difference!
I recently trialled the Gold Dust along with the Algae oil with a 9 year old 40 kg English Bulldog that I look after who was struggling to lift his back legs to pee and go up and down the stairs
Kissy developed urinary tract problems
She was advised to go onto Royal Canin S/O which is high in wheat and corn gluten, animal fats, hydrolysed animal proteins, crushed shellfish, fish oil, soya oil and dehydrated poultry – nothing kind that suited Kissy!
Prof Andrew Knight’s studies continue!
Prof Knight’s latest study shows the remarkable environmental impact of dogs, cats and us going vegan and how it could quite literally save the planet!